Fire-Rated Glass
in Health Care
Explore our tools and insights to design safer, code-compliant health care facilities - stat.
Diagnosing design
Challenges in Health
Care settings
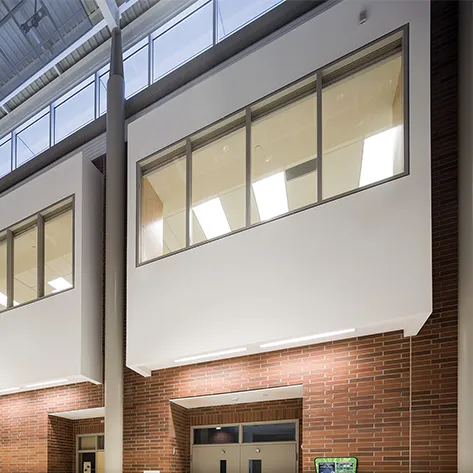
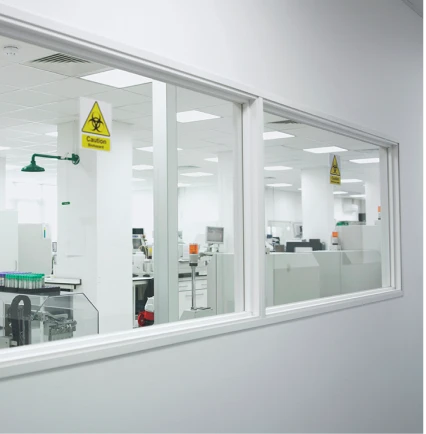
In many areas of a medical building, fire-rated materials are required to create barriers that defend against fire, smoke and radiant heat. However, visual connection, access to daylight and more easily navigable spaces are often crucial to creating more functional health care settings. Learn how fire-rated glass can support both code-compliant and occupant-centered designs.
Patient Safety and
compartmentalization
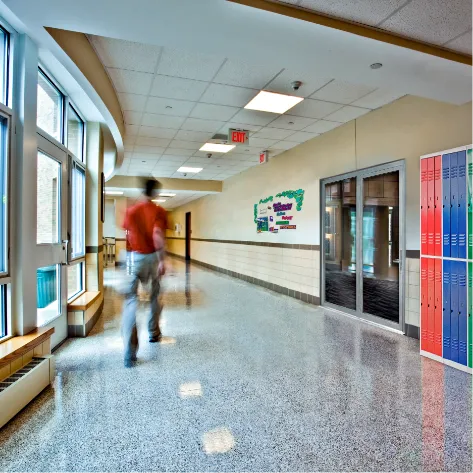
In health care environments, occupant mobility limitations and cognitive impairments make compartmentalization essential.
- Many patients have limited mobility or cognitive impairments, making safe evacuation challenging.
- Compartmentalization helps contain fire, smoke, and heat to specific areas.
- Fire-rated glass for hospitals enables open, light-filled environments while enhancing life safety.
- Proper specification helps meet strict health care fire code requirements.
Balancing safety with
patient wellbeing
While life safety is paramount, design considerations must also prioritize occupant comfort and health outcomes:
- Daylight Access: Studies show that exposure to natural light enhances patient recovery rates and overall wellbeing. Fire-rated glass solutions with high clarity and minimal visual obstruction ensure that daylight flows through interior spaces.
- Visibility for Care Providers: Clear, fire-rated glazing enhances sightlines, enabling staff to monitor patients effectively while maintaining fire protection. These systems are also available with integrated blinds for applications where patient privacy is also important.
Design Prognosis:
Code-Compliant AND
Occupant-Centered
Where can architects and specifiers achieve code compliance without sacrificing occupant wellbeing in health care facilities? Explore the applications of fire-rated glass in creating safer, more connected health care spaces while adhering to strict fire and life safety standards.

Fire-rated glass in stairwells can meet means of egress requirements in a wide range of health care settings and bring daylight into hard-to-illuminate spaces.

Fire-rated curtain walls in health care environments can support compartmentalization without compromising access to daylight.

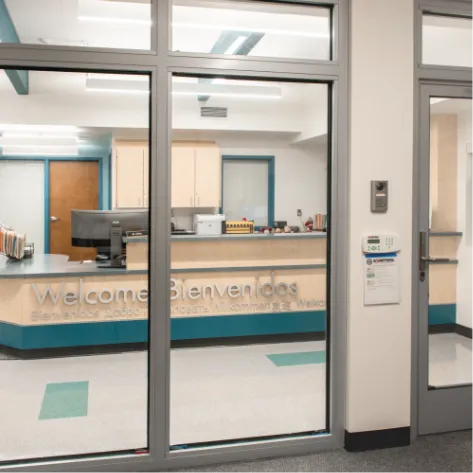
Fire-rated glass partitions maintain code-driven requirements while supporting ease of wayfinding and navigability.

Fire-rated glass doors in health care meet free egress requirements in stairwells, patient rooms, labs and more.

Fire-rated glass in hospitals can balance visual connection and privacy, especially when used as side and vision lites in patient room doors.

Impact-and fire-rated glass in health care can contribute to safer behavioral health environments for patients and providers.
Connect with a TGP expert in your area about integrating fire-rated glazing into your next health care building project.
The Basics: FIRE-RATED GLASS AND FRAMING AND SPECIALTY GLAZING
Fire
Q. How do I learn more about fire-rated glazing?

A. Fire-rated and specialty glazing allow health care designs that were previously unattainable due to fire- and life-safety codes. But building professionals may have questions about how to use these systems most effectively.
Explore Fire-Rated Basics to find answers to common questions about fire-rated systems and design.
Radiation Shielding
Q. What is the difference between X-ray shielding and Gamma-ray shielding glass?

A. In addition to fire-rated designs, some applications in health care facilities may require protection from radiation. These include radiology departments, nuclear medicine labs, radiation suites, CT scan rooms and more.
Radiation shielding glass is categorized based on its lead oxide and heavy metal oxide content. X-ray shielding glass commonly has a heavy metal oxide content of 60 percent with 55 percent being lead oxide. Because more heavy metals are necessary for Gamma-ray shielding, this type of specialty glazing has a heavy metal oxide content of 70 percent, which is equivalent to ultra-high lead content block glass for nuclear power facilities.
TGP offers three types of radiation-protective glass including LX X-Ray, LX Premium and Pro-GR Gama Ray Shielding glass.
Beyond The Basics: fire-rated glass and framing for health care applications
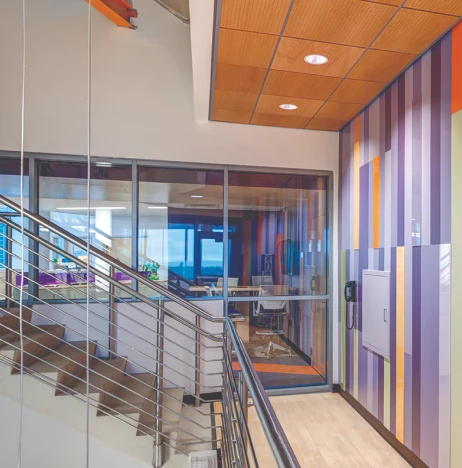
PRESCRIPTION FOR SAFETY: fire-rated stairwell provides light and life safety for medical center
Design intended to provide clinical researchers and hospital staff visual connectivity between spaces and access to natural light.
Get the StoryImprove health care
with specialty glass
The design of health care facilities often needs to incorporate specialty materials to ensure the building is code-compliant and safe for operation.
Read MoreCreating safer spaces:
a deep dive into bullet-resistant glass
Forced entry- and bullet-resistant glass have seen increased use in multiple occupancy types.
See the ArticleProducts
And Solutions
Discover a variety of fire-, fire + forced-entry-, and specialty-glazing options to support code-compliance and push design options forward in health care centers. Custom solutions from Technical Glass Products can meet multiple, critical-functionality requirements without compromising aesthetics. These glazing systems contribute to occupant-centered health care designs.
Health Care Building Design Resources

Expert Insights
Best Practices Recommendations and Code-Compliant Health Care
Best Practices Recommendations and Code-Compliant Health Care
Health care design can be complex. Retrofit projects and new builds alike must meet a wide range of code requirements, which are often more stringent than other occupancies. On the one hand, this is b...
>>

Article
Fire protection devices offer complex solutions
Fire protection devices offer complex solutions
Publication: Healthcare Facilities Management
>>

Case Study
Cincinnati Children's Medical Center, Clinical Services Pavilion
Cincinnati Children's Medical Center, Clinical Services Pavilion
Cincinnati, OH
>>
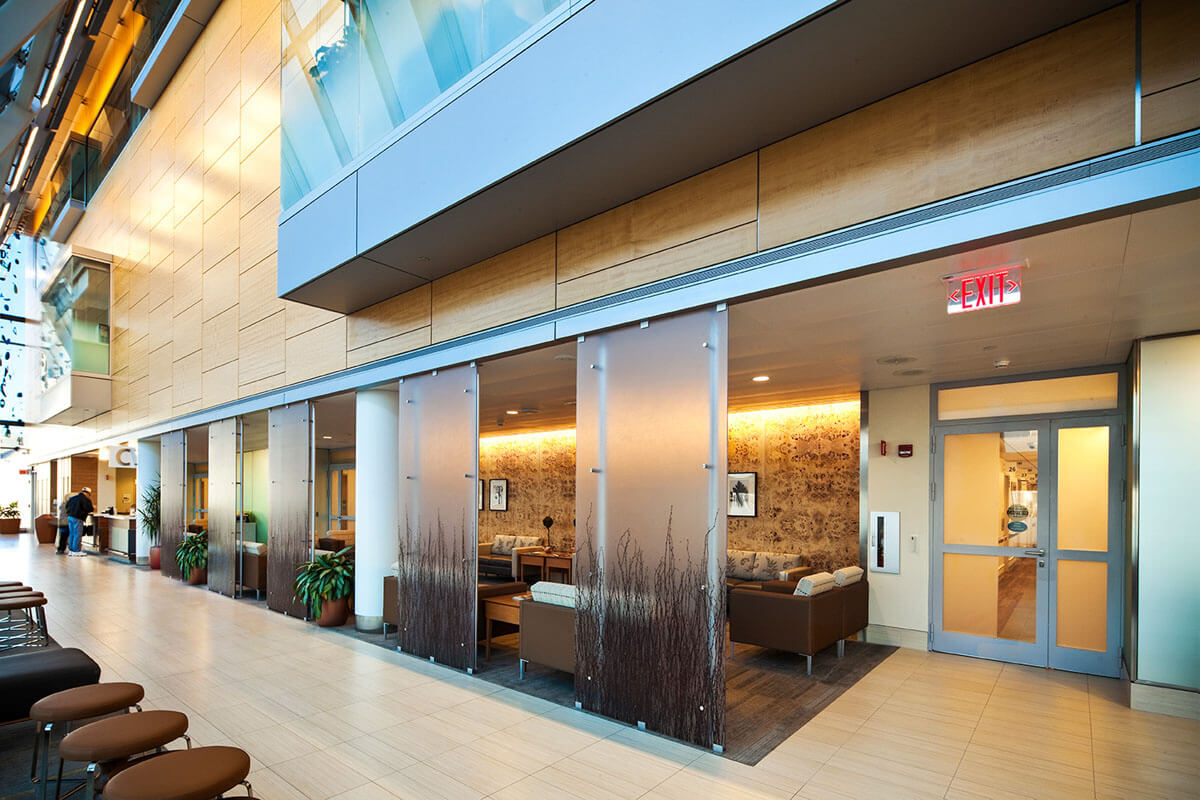

Case Study
University Hospitals Seidman Cancer Center
University Hospitals Seidman Cancer Center
Cleveland, OH
>>
Design Resource
Fire-Rated Basics

Design Resource
Fire-Rated Door Design
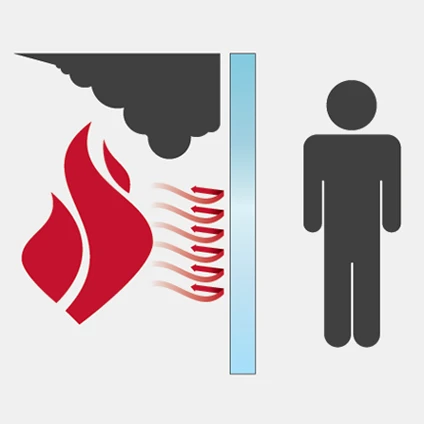

Product Selection
Product Comparison

Design Resource
Look Book
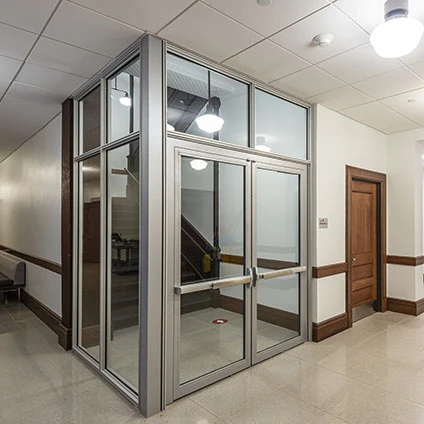

Design Resource
Matched Systems
Care for every detail
Take our AIA-registered course to better understand fire-rated glazing basics and earn I LU/HSW Hour.
Take CourseSpecifire®
Not sure which products are right for your health care project? We’ll help you decide with our interactive tool.
Learn moreCommercial sliding doors
Visit AD Systems, our sister brand site, to learn more about their high performing sliding doors for health care applications.
Go To Site